

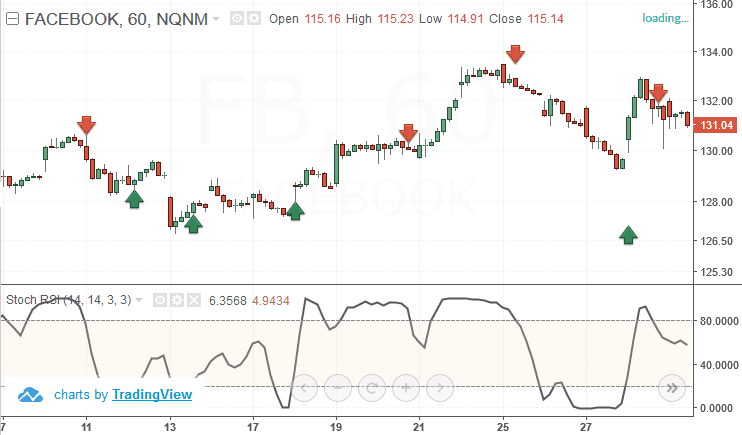
The excess of current assets over current liabilities provides a measure of safety margin available against uncertainty in realisation of current assets and flow of funds. A very high current ratio is not a good sign as it reflects under utilisation or improper utilisation of resources. Every company must ensure that part of its assets are liquid in case it needs money right now. As a result, ratios like the current ratio and the quick ratio are used to assess a company’s liquidity.
These aid a company’s ability to sustain the necessary degree of short-term solvency. The gross profit ratio expresses the proportion of factory costs to sales revenue.A higher gross profit margin shows that a company’s operations are more efficient. On the other hand where stock contributes a reasonably less amount it can be avoided and liquidity of that firm can be measured with the help of quick ratio. This is because, the heavy stocks like machinery, heavy tools etc. cannot be easily sold off.
Here the long term obligation means payments of principal amount on the due date and payments of interests on the regular basis. For measuring the long term solvency of any business we calculate the following ratios. Accounting ratios are very helpful in analyzing any company’s performance but on the flip side, these ratios calculated using balance sheet on a specific date.
Pretax Income is a made up of two sources, income from assets funded by shareholders equity, and assets funded by borrowed debt. Leverage of Assets measures the ratio between assets and owner's equity of a company. The Debt Ratio indicates what proportion of debt a company has relative to its assets.
Quick Link
It is critical for an analyst to be aware of these potential manipulations and to conduct thorough due diligence before drawing any conclusions. If the company’s accounting standards and practices have changed, this could have a significant impact on financial reporting. The key financial indicators used in ratio analysis are changed in this scenario, and the financial outcomes reported after the change are not comparable to those recorded before the change.
Days Receivables indicates the average number of days that receivables are outstanding. High numbers indicate long collection periods, low numbers indicate efficient collection of receivables. Earnings Per Share is the portion of a company's profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock. The Return on Invested Capital measure gives a sense of how well a company is using its money to generate returns. Comparing a company's return on capital with its cost of capital reveals whether invested capital was used effectively.
They convert the financial statement into comparison statistics, allowing management to assess and evaluate the firm’s financial status and the outcomes of their decisions. In addition, the accounting numbers used to calculate ratios should be related in some way. This is because a financial examination of the company’s financial outcomes would be meaningless if the statistics were unrelated. Leveraged Assets Contribution to NI is the percentage of the pretax income that is provided by management’s use of debt to fund assets. Negative number show losses generated by the assets financed by debt.
Accounting Ratios
Use the Asset Turnover Calculator to calculate the asset turnover and Du Pont ratios from your financial statements. Use the Debt Ratio Calculator to calculate the debt ratio from your financial statements. Fixed Asset Turnover measures the efficiency of fixed assets to generate profit. The higher the number, the more efficient management’s use of fixed assets.
Surface profile analysis of laminated transfemoral prosthetic socket … – Nature.com
Surface profile analysis of laminated transfemoral prosthetic socket ….
Posted: Wed, 15 Feb 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Use the Price to Earnings Ratio Calculator above to calculate the price to earnings ratio from your financial statements. Use the Debt Servicing Ratio Calculator above to calculate the debt servicing ratio from your financial statements. Use the Debt to Tangible Net Worth Calculator above to calculate the debt to tangible net worth from your financial statements. Use the Fixed Asset Turnover Calculator to calculate the fixed asset turnover from your financial statements. Use the Inventory Turnover Calculator to calculate the inventory turnover from your financial statements. Use the Accounts Receivable Turnover Calculator to calculate the accounts receivable turnover from your financial statements.
Accounts and Audit
Return on https://1investing.in/ is an indicator of how profitable a company is relative to its total assets. ROA gives an idea as to how efficient management is at using its assets to generate earnings. Use the Quick Ratio Calculator above to calculate the quick ratio from your financial statements.
- Use the Price to Earnings Ratio Calculator above to calculate the price to earnings ratio from your financial statements.
- Generally higher stock ratio can be the result of deficit of working capital and lower stock – ratio can be the result of unnecessary investment in working capital.
- In addition, the accounting numbers used to calculate ratios should be related in some way.
- Turnover and efficiency ratios will highlight any asset mismanagement.
It helps to identify the financial stability of the business by analyzing the total debt of the company. Because financial statements are released on a regular basis, there are time gaps between them. Real prices are not represented in the financial accounts if inflation has occurred between periods. As a result, until the figures are corrected for inflation, they are not comparable across time periods.
That’s why composite ratios show turnover ratio is more important in case of grocery store than an insurance company. For a company, gross profit and credit sales are ₹ 1,20,000 and ₹ 4,80,000 respectively. The information given by the corporation in its financial accounts is the basis for ratio analysis. This data could be modified by the company’s management to show a greater performance than it actually has. As a result, ratio analysis may not adequately reflect the underlying nature of the firm, because information misrepresentation is not detectable by basic analysis.
Use the Asset turnover calculator above to calculate the asset turnover from your financial statements. Return on Equity provides the amount of net income returned as a percentage of shareholders equity. Return on equity measures a corporation's profitability by revealing how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested. Use the Return on Assets Calculator above to calculate the profitability ratio from your financial statements. Gross profit would be the difference between net sales and cost of goods sold. Cost of goods sold in the case of a trading concern would be equal to opening stock plus purchase, minus closing stock plus all direct expenses relating to purchases.
The second one is considered the more refine form of measuring the liquidity of the firm. The current ratio provides a better measure of overall liquidity only when a firm’s inventory cannot easily be converted into cash. If inventory is liquid, the quick ratio is a preferred measure of overall liquidity. 2,50,000, financial cost ₹ 1,50,000 and sales ₹ 30,00,000 then find out operating profit ratio. Accounting ratio is the comparison of two or more financial data which are used for analyzing the financial statements of companies. It is an effective tool used by the shareholders, creditors and all kinds of stakeholders to understand the profitability, strength and financial status of companies.
- Return on equity measures a corporation's profitability by revealing how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested.
- Analysts can use activity ratios to assess a company’s inventory management, which is critical to its operational flexibility and overall financial health.
- High numbers indicate long collection periods, low numbers indicate efficient collection of receivables.
- Days Receivables indicates the average number of days that receivables are outstanding.
Furthermore, in order to make important financial decisions, business owners, analysts, and other stakeholders examine, compare, and interpret this financial data. However, such information is interpreted using financial statement analysis tools and methodologies. In this article, we have covered each type of accounting ratios, their formula, and importance of each ratio. A company’s assets can be divided into assets funded by equity, and assets funded by debt.
It is the analyst’s responsibility to keep up with changes in accounting policies. The notes to the financial statements section usually contain the changes made. They can tell if a company’s assets are being strained or if the company is over-leveraged. To avoid liquidation in the future, management will need to immediately correct the situation. Debt-Equity Ratios, Leverage Ratios, and other similar ratios are examples.
In this case it is always advisable to follow the current ratio for measuring the liquidity of a firm. In a company, cost of goods sold ₹ 6,40,000; current assets ₹ 4,80,000; current liabilities ₹ 1,60,000 and gross profit rate on sales is 20% then find out working capital turnover. RatioFormulaObjectiveAccounts Receivable RatioThe ability of a business to collect money from its clients is determined by the accounts receivable turnover ratio. For a given period, total credit sales are divided by the average accounts receivable balance. Financial statements contain financial information about a company’s financial situation.

The decreasing trend of operating ratio suggest the increase in profitability. For useful interpretation of financial statement, comparison is included in ratio analysis. A company’s operational structure, from its supply chain strategy to the product it sells, may undergo major changes. Use the Sustainable Growth Rate Calculator to calculate the sustainable growth rate from your financial statements. Sustainable Growth Rate is the maximum growth rate of a company if none of its ratios change and it does not raise new capital through selling shares. Profit Margin is used to determine the profitability of each dollar of sales that company makes.